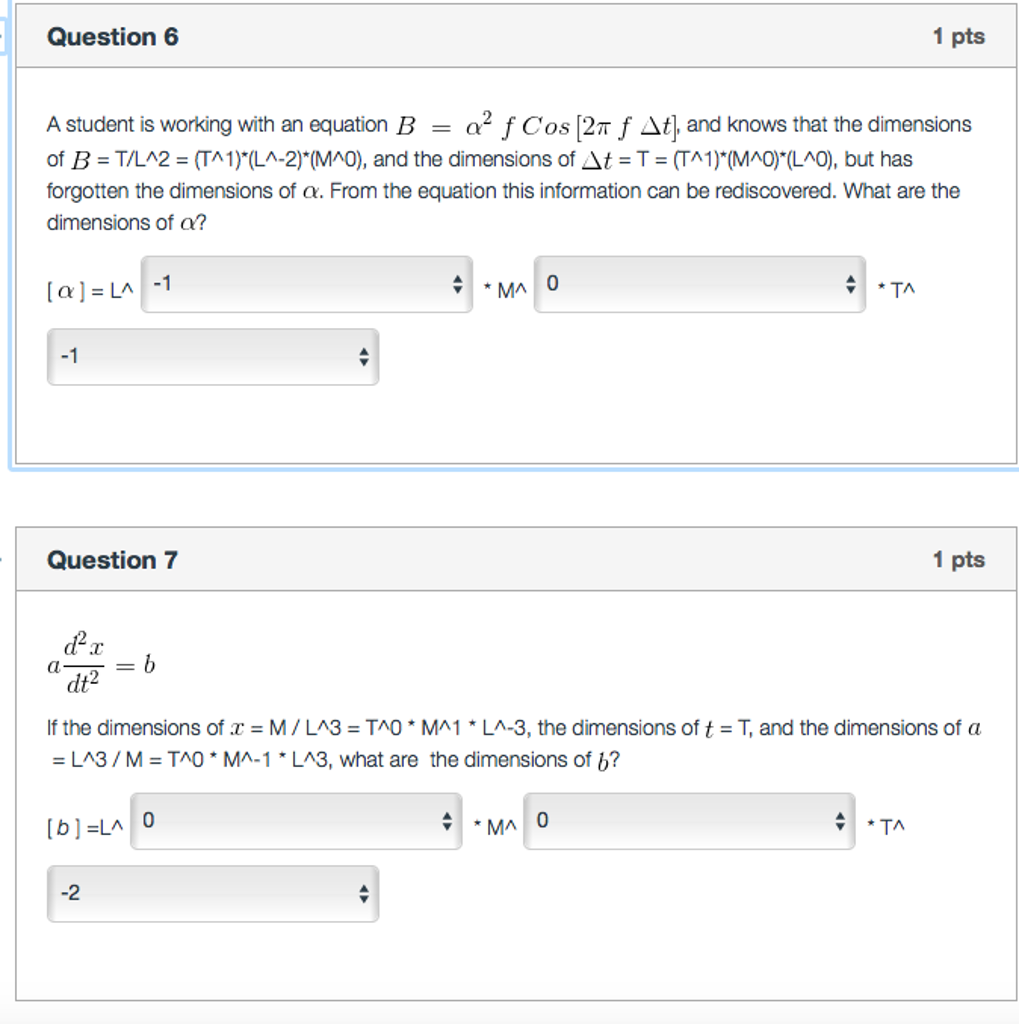
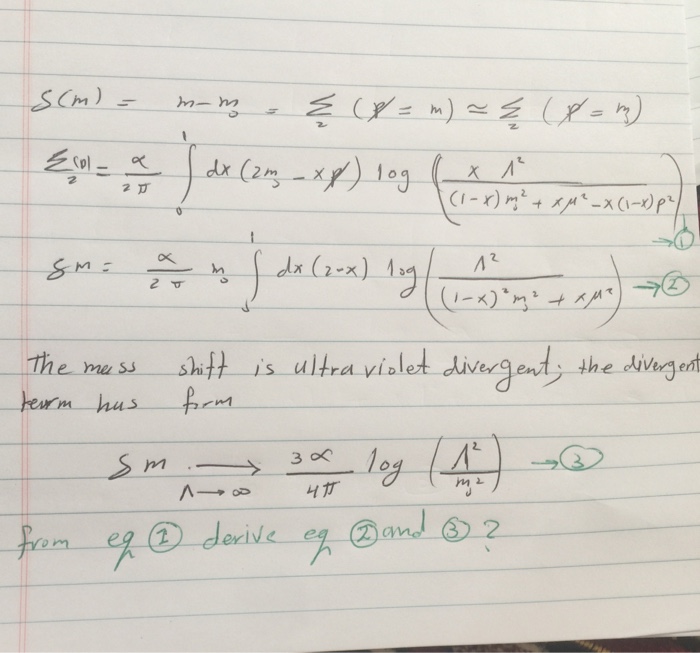![The expression 3 [ sin ^4 { 3pi2 - alpha } + sin ^4 (3pi + alpha ) ] - 2 [ sin ^6 ( pi2 + alpha ) . + sin ^6 (5pi - alpha )] is equal to : The expression 3 [ sin ^4 { 3pi2 - alpha } + sin ^4 (3pi + alpha ) ] - 2 [ sin ^6 ( pi2 + alpha ) . + sin ^6 (5pi - alpha )] is equal to :](https://haygot.s3.amazonaws.com/questions/1257510_1327617_ans_4a5fe128582147d48f5973059510176e.PNG)
The expression 3 [ sin ^4 { 3pi2 - alpha } + sin ^4 (3pi + alpha ) ] - 2 [ sin ^6 ( pi2 + alpha ) . + sin ^6 (5pi - alpha )] is equal to :

Let f : (0, pi)→ R be a twice differentiable function such that limit t→x f(x)sint - f(t)sinxt - x = sin^2x for all xepsilon (0, pi) .If f (pi6) = -

If sin A = 4/5,pi/2<A<pi and cos B = 5/13,3pi/2<B<2pi , find (i) sin (A + B) , (ii) cos (A - B) , (iii) tan (A - B)
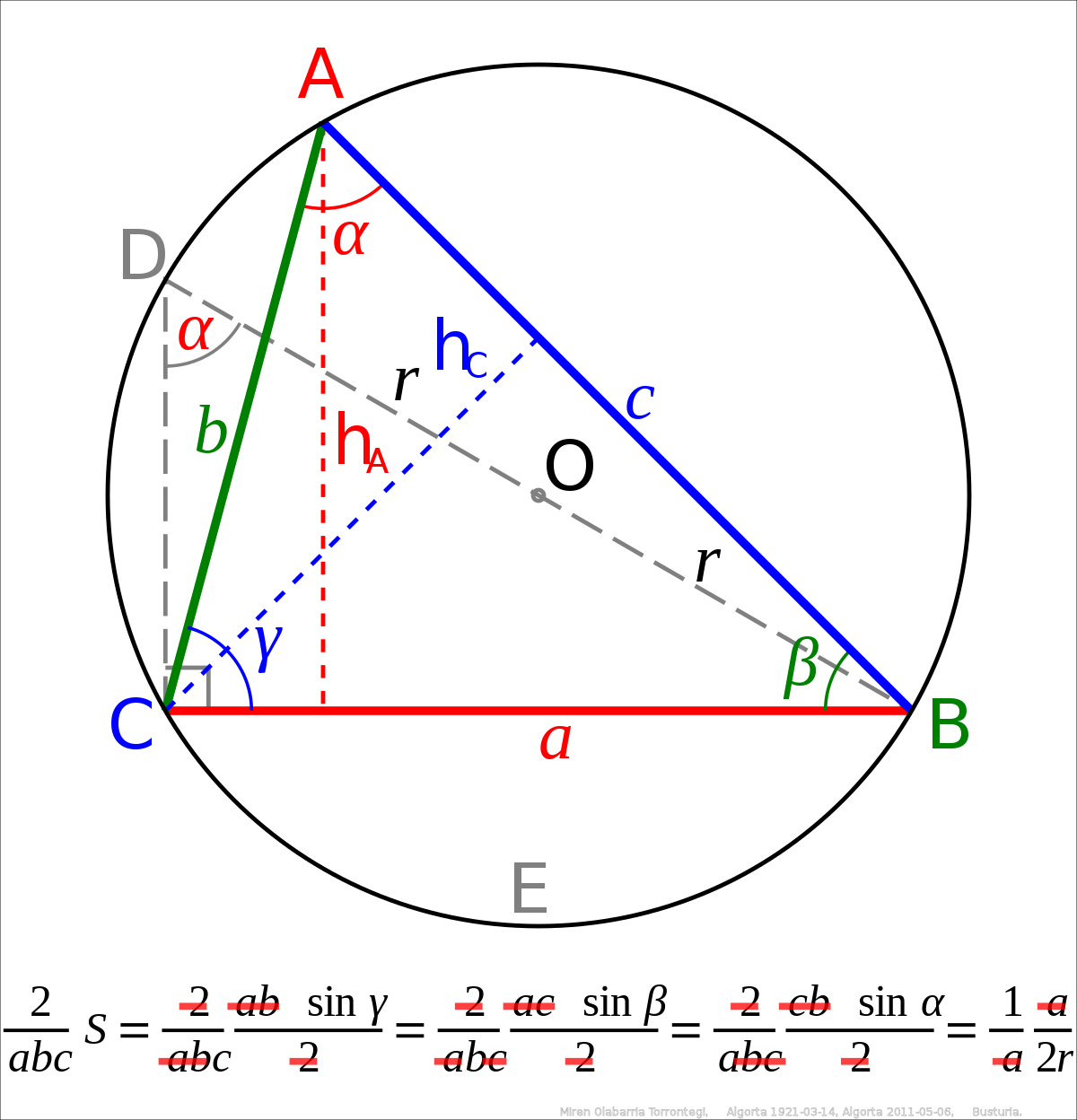
![Let f:R -> ( 0,(2pi)/2] defined as f(x) = cot^-1 (x^2-4x + alpha) Then the smallest integral value of alpha such that, f(x) is into function is Let f:R -> ( 0,(2pi)/2] defined as f(x) = cot^-1 (x^2-4x + alpha) Then the smallest integral value of alpha such that, f(x) is into function is](https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.cloudfront.net/ss/web/1668560.jpg)
Let f:R -> ( 0,(2pi)/2] defined as f(x) = cot^-1 (x^2-4x + alpha) Then the smallest integral value of alpha such that, f(x) is into function is